Diagram and Table Completion Questions
Another type of question you may face is a diagram completion question.
Take a look comparison of the two below:
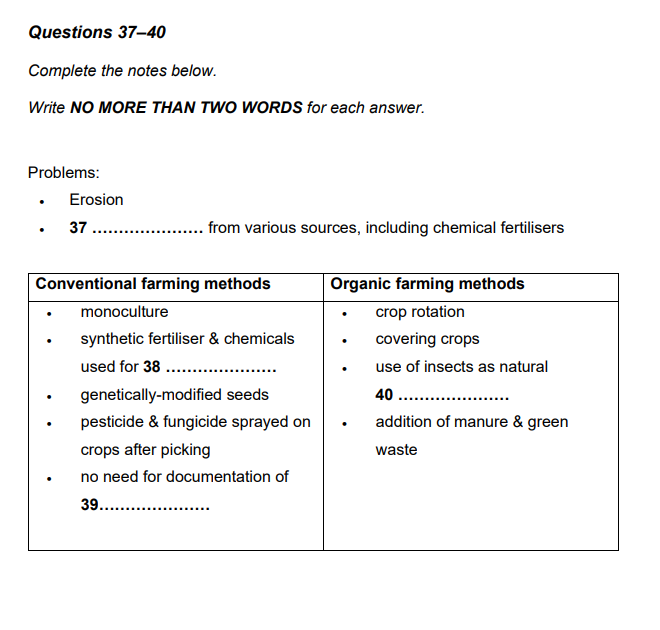

Differences between Diagram and Table completion and notes
What differences are there between diagram and table completion questions compared to the notes style questions in the previous lesson?
Differences
- Table/diagram questions do not have continuous prose. Note questions have longer text to read and understand.
- Diagram/Table questions have visuals to assist you slightly.
- quite importantly, the questions do not appear in a linear order. In the notes style of question items all come in order, one after the other (4, 5, 6 etc). However this is not necessarily the case for diagram questions. For example you could see the items in order of 35, 34, 33.
Note: the information will always come in order, even if the layout of the questions is not. Example: On the page the questions show as q.35. at the top, then 34. and 33. at the bottom, the information will always come in order. You will hear the answer according to question number, not position on the page. (so you will hear in order 33,34.35)
similarities
- The instructions are similar
- Information in the audio comes in order of the question numbers.
- You can prepare by looking around the gaps for textual clues to identify missing parts of speech
- You can try predicting logical answers
- You can begin listening for keywords to know when an answer is coming up
Diagram completion suggested strategy
- Read instructions carefully.
- Skim read the diagram to get an idea of what it’s about
- Identify the flow of answers and what you’ll hear first.
- Look around the gaps/at other examples to identify missing parts of speech.
- Try to predict possible answers.
- Look for keywords which indicate when it’s time to move on and listen carefully
for these. - Listen and write EXACTLY what the speaker says in answers, paying attention
to the word limit of the instruction
Table completion suggested strategy
- Read instructions carefully.
- Skim read the column/row headings to get an idea of what it’s about.
- Identify the flow of answers and what you’ll hear first
- Look around the gaps/at other examples to identify missing parts of speech
- Try to predict possible answers
Look for keywords which indicate when it’s time to move on and listen carefully
for these - Listen and write EXACTLY what the speaker says in answers, paying attention
to word limit of the instruction.


